“10 Key Insights into Australia’s Employment and Wage System – 2025 Update
Explore job opportunities, wage structures, benefits, and in-demand sectors like Social Work, Healthcare, and Community Services.”
Are you exploring the Australian job market? This article outlines 10 essential facts about Australia’s employment and wage system, with a spotlight on Social Work, Healthcare, and Community Services – sectors facing skills shortages, offering stable income and strong benefits.
1. Australia’s Labour Market Overview: A Land of Opportunities
Australia boasts one of the world’s most developed and resilient economies, offering diverse job opportunities for both locals and international workers. The country consistently maintains a low unemployment rate, reflecting a dynamic labour market.
- Flexibility: The labour market allows individuals to change jobs or careers with the right skills and experience.
- Industry Diversity: High demand across various sectors – from engineering, IT, finance, to tourism, education, healthcare, and community services.
- Government Support: Job seekers benefit from vocational training programs, employment services, and unemployment support.
To learn more, visit the Australian Government’s Department of Employment and Workplace Relations.

10 Things to Know About Australia’s Employment and Pay System
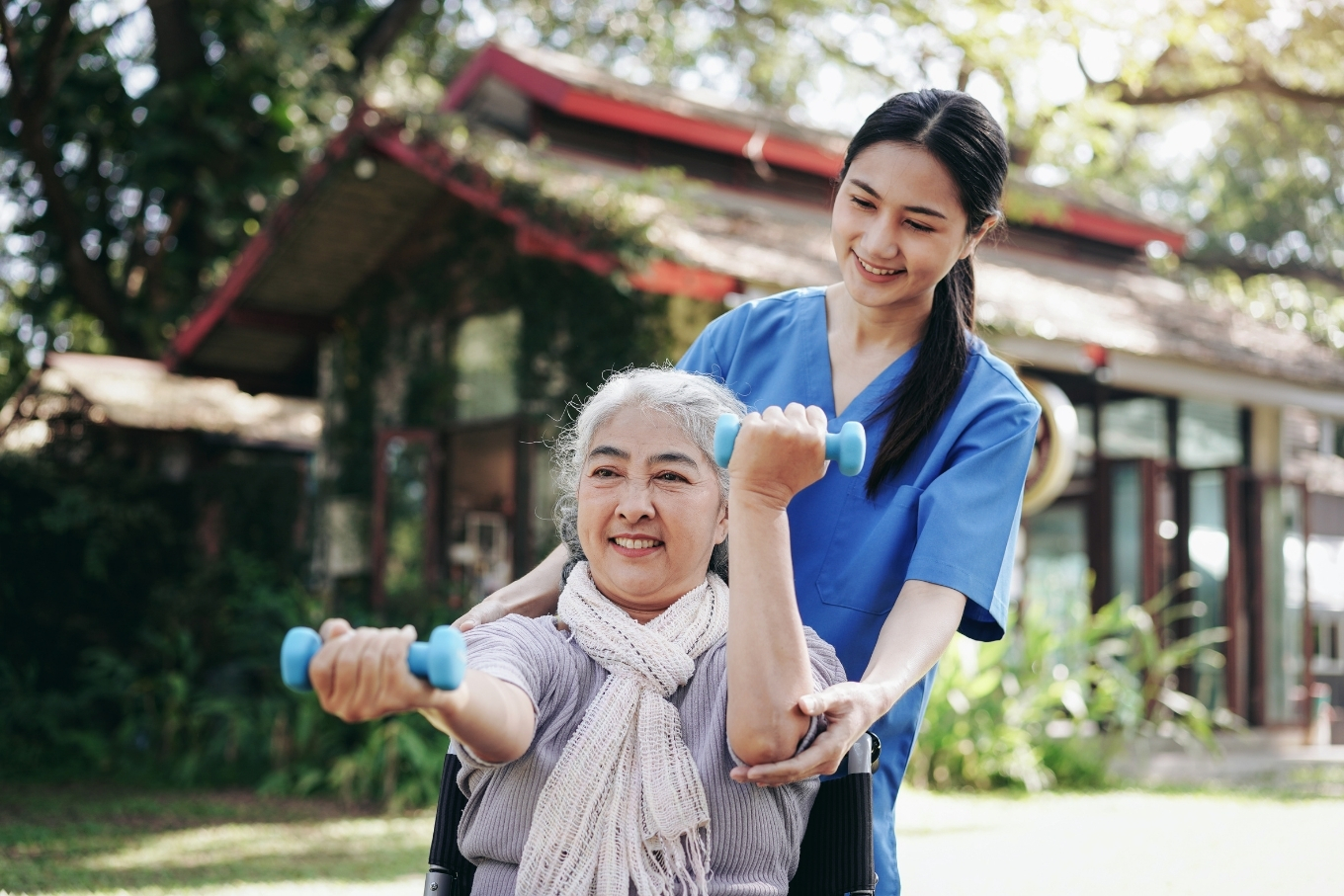
2. High-Demand Sectors: Social Work, Healthcare & Community Services
With an ageing population and increasing social needs, Australia has seen soaring demand in:
- Social Work: Especially in child protection, disability support, aged care, and vulnerable community services.
- Healthcare: Nurses, doctors, pharmacists, physiotherapists, and mental health professionals are in continuous demand.
- Community Services: Includes roles in community support, counselling, education, and program development.
These sectors offer stable careers, deep societal impact, and are part of Australia’s Priority Migration Skilled Occupation List – making them ideal for those seeking long-term settlement.
3. National Minimum Wage (2025 Update)
Wages in Australia are typically calculated hourly or annually. As of 1 July 2025, the national minimum wage is:
- $24.95 AUD/hour or $948.00 AUD/week (based on 38-hour work week).
- Industry-specific wages vary based on profession, experience, location, and employer type.
For official updates, refer to the Fair Work Commission.
4. Wage Structures: Award, Enterprise, and Individual Agreements
Australia’s wage system is governed by three key mechanisms:
- Modern Awards: Set minimum pay rates and conditions for specific industries or occupations.
- Enterprise Agreements: Negotiated between employers and employees (or unions), tailored to individual workplaces.
- Individual Agreements: Used mainly for senior or specialist roles, provided they comply with national standards.
Understanding which agreement applies to your role ensures fair pay and working conditions.

5. Superannuation (Super): Your Retirement Savings
Superannuation is a compulsory retirement fund contribution made by employers on top of your wage.
- Contribution Rate: Set and regulated by the government.
- Purpose: To support you financially in retirement.
- Your Rights: You can choose your super fund and track contributions.
Learn more at the Australian Taxation Office (ATO).
6. Leave Entitlements: Work-Life Balance Matters
Australian employees enjoy several types of paid and unpaid leave:
- Annual Leave: 4 weeks of paid leave per year for full-time employees.
- Personal/Carer’s Leave: For illness or caring responsibilities.
- Public Holidays: Paid leave for national and state-recognised holidays.
- Parental Leave: For new parents (birth or adoption).
- Compassionate Leave: When a family member passes away.
Details available from the Fair Work Ombudsman.
7. Personal Income Tax: What You Need to Know
Australia applies a progressive income tax system:
- Higher income = higher tax rate.
- You’ll need a Tax File Number (TFN) to work legally.
- Annual tax returns must be filed with the ATO.
Visit the Australian Taxation Office for updated tax thresholds and guides.
8. Work Health and Safety (WHS): Safety First
Workplace health and safety is a legal requirement in Australia:
- Strict legislation is enforced to prevent accidents and occupational illness.
- Rights & Responsibilities: You’re entitled to a safe workplace and must report hazards.
- Training: Many roles require mandatory WHS training.
Find out more via Safe Work Australia.
9. Challenges & Opportunities: NextGem’s Advice
From our experience, navigating Australia’s job and wage system can be challenging for newcomers. But with preparation, the opportunities are vast.
- Challenges: Workplace culture differences, legal complexity, and competitive job market.
- Opportunities: High demand industries, strong worker protections, and long-term career growth.
Tips from NextGem:
- Research your target industry, wage expectations, and qualification requirements.
- Build a professional network – connect with Vietnamese and industry communities in Australia.
- Improve your skills – focus on English, soft skills, and certifications.
10. Career & Migration Planning: Think Long-Term
Employment and salary are only part of the journey. Successful migration requires a clear pathway:
- Choose the right occupation: Prioritise in-demand and PR-listed roles.
- Get the right visa: Such as Skilled Visas or Employer Sponsored Visas.
- Seek expert advice: Work with reputable migration or education consultants for tailored guidance.
>> NextGem is here to support your journey.
With extensive experience in education, employment, and migration to Australia, we provide up-to-date information and customised pathways.
Contact us today to start planning your study–work–migration journey in Australia.